Demand-Supply Analysis - Explained
What is a Demand Supply Analysis?
- Marketing, Advertising, Sales & PR
- Accounting, Taxation, and Reporting
- Professionalism & Career Development
-
Law, Transactions, & Risk Management
Government, Legal System, Administrative Law, & Constitutional Law Legal Disputes - Civil & Criminal Law Agency Law HR, Employment, Labor, & Discrimination Business Entities, Corporate Governance & Ownership Business Transactions, Antitrust, & Securities Law Real Estate, Personal, & Intellectual Property Commercial Law: Contract, Payments, Security Interests, & Bankruptcy Consumer Protection Insurance & Risk Management Immigration Law Environmental Protection Law Inheritance, Estates, and Trusts
- Business Management & Operations
- Economics, Finance, & Analytics
What is a Demand-Supply Analysis?
In a market economy, the level of demand and supply of all goods and services jointly determines the price level and quantity of that good (or service) in the economy.
When to Use Supply Demand Analysis?
The law of demand states that (with a few exceptions) as price rises, the quantity demanded of any good or service would be lower.
The law of supply implies that higher the price received by a supplier, the quantity supplied will rise. Thus, demand is often a downward sloping curve in the price-quantity plane, while supply is an upward sloping curve.
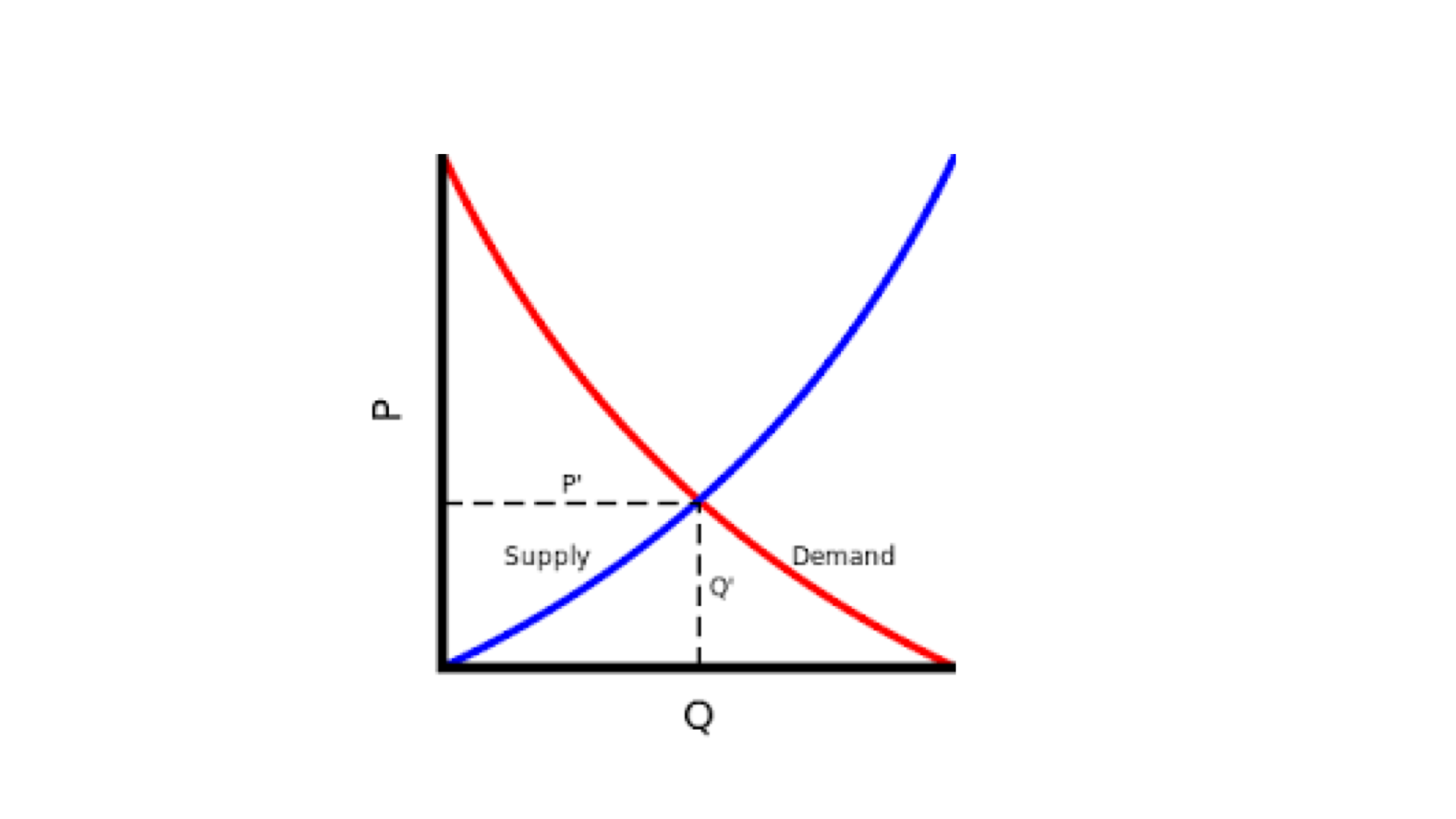
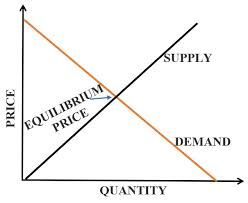
What is the Equilibrium Price?
The intersection of the supply and demand curve denotes the market equilibrium, which in turn determines the equilibrium levels of price and quantity of the particular good (or service) in the economy.
If the present demand for a good (or service) in the economy is higher than the equilibrium quantity, the situation is described as that of an excess demand. Excess supply is also defined in a similar fashion.
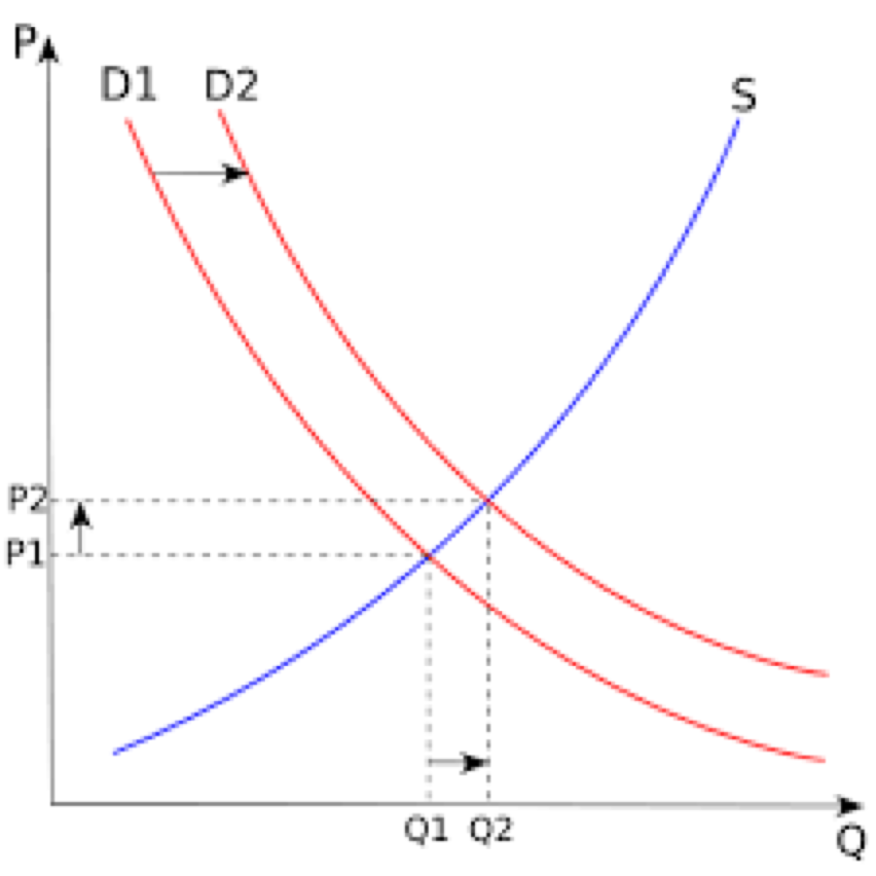
What Causes Shifts in Supply or Demand?
Changes in Supply and demand (and thus the equilibrium price and quantity) of any good or service could be governed by a lot of factors, such as: changes in policies, unpredictable shocks to the economy, business cycle fluctuations like a recession or a boom, or even simply over time (long run versus short run). It also depends on the nature of the market (whether the market is perfectly competitive or monopolistic etc.).
The analysis of all the above could be termed as the study of the supply and demand, or simply, 'Demand Supply Analysis'.
Related Topics
- Self Interest
- Cost-Benefit Analysis
- Enlightened Self-Interest
- Fisher's Separation Theorem
- Ratchet Effect
- Total Utility (Economics)
- Efficiency Principle
- Expected Utility
- Subjective Theory of Value
- Positional Goods
- Utilitarianism
- Indifference Curve
- Time Preference Theory of Interest
- Incentives
- Marginal Benefit
- Diminishing Marginal Utility
- Sunk Costs
- Production Possibilities Frontier
- Law of Diminishing Returns
- Economic Efficiency
- Efficiency Theory
- Productive Efficiency
- Capacity Utilization Rate
- Allocative Efficiency
- Pareto Efficient
- Comparative Advantage
- Criticisms of the Economic Approach
- Behavioral Economics
- Normative Economics
- Positive Economics
- Invisible Hand
- Sunk cost