First Rule of Labor Markets
What is the First Rule of Labor Markets?
- Marketing, Advertising, Sales & PR
- Accounting, Taxation, and Reporting
- Professionalism & Career Development
-
Law, Transactions, & Risk Management
Government, Legal System, Administrative Law, & Constitutional Law Legal Disputes - Civil & Criminal Law Agency Law HR, Employment, Labor, & Discrimination Business Entities, Corporate Governance & Ownership Business Transactions, Antitrust, & Securities Law Real Estate, Personal, & Intellectual Property Commercial Law: Contract, Payments, Security Interests, & Bankruptcy Consumer Protection Insurance & Risk Management Immigration Law Environmental Protection Law Inheritance, Estates, and Trusts
- Business Management & Operations
- Economics, Finance, & Analytics
What is the First Rule of Labor Markets?
The labor market, like all markets, has a demand and a supply. Why do firms demand labor? Why is an employer willing to pay you for your labor? It’s not because the employer likes you or is socially conscious. Rather, it’s because your labor is worth something to the employer--your work brings in revenues to the firm. How much is an employer willing to pay? That depends on the skills and experience you bring to the firm.
If a firm wants to maximize profits, it will never pay more (in terms of wages and benefits) for a worker than the value of his or her marginal productivity to the firm. We call this the first rule of labor markets.
Suppose a worker can produce two widgets per hour and the firm can sell each widget for $4 each. Then the worker is generating $8 per hour in revenues to the firm, and a profit-maximizing employer will pay the worker up to, but no more than, $8 per hour, because that is what the worker is worth to the firm.
Recall the definition of marginal product. Marginal product is the additional output a firm can produce by adding one more worker to the production process. Since employers often hire labor by the hour, we’ll define marginal product as the additional output the firm produces by adding one more worker hour to the production process. In this chapter, we assume that workers are homogeneous—they have the same background, experience and skills and they put in the same amount of effort. Thus, marginal product depends on the capital and technology with which workers have to work.
A typist can type more pages per hour with an electric typewriter than a manual typewriter, and he or she can type even more pages per hour with a personal computer and word processing software. A ditch digger can dig more cubic feet of dirt in an hour with a backhoe than with at shovel.
Thus, we can define the demand for labor as the marginal product of labor times the value of that output to the firm.
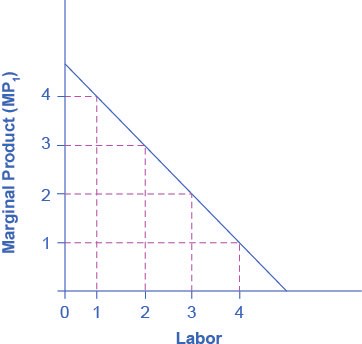
On what does the value of each worker’s marginal product depend? If we assume that the employer sells its output in a perfectly competitive market, the value of each worker’s output will be the market price of the product. Thus,
Demand for Labor = MPL x P = Value of the Marginal
Note that the value of each additional worker is less than the ones who came before.
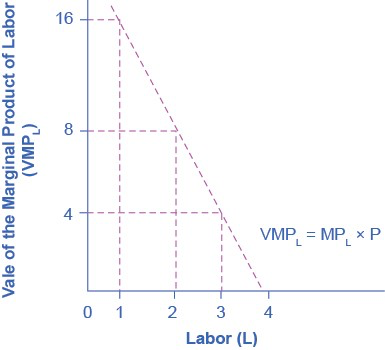
For firms operating in a competitive output market, the value of additional output sold is the price the firms receive for the output. Since MPL declines with additional labor employed, while that marginal product is worth the market price, the value of the marginal product declines as employment increases.
Related Topics
- Labor Economics
-
Labor Market Equilibrium
- Labor Market
- Labor Market Equilibrium
- Labor Market Efficiency
- Price, Supply, and Demand in the Labor Market
- Equilibrium Wage
- Shifts in the Demand for Labor
- What Causes Shifts in the Supply Labor?
- How Technology affects Demand for Labor?
- Minimum Wage as a Price Floor in the Labor Market
- What is the First Rule of Labor Markets?
- Labor Demand in Perfectly Competitive Markets
- Imperfect Competition in Labor Markets
- Monopsony
- Oligopsony
- Labor Market Power of Employers
- What is the marginal Cost of Labor?
- Labor Market Power of Employees
- What is a Bilateral Monopoly in a Labor Market?
- Wage Elasticity of Labor Supply
- Equilibrium in Supply and Demand in Labor Markets
- Shifts in Supply and Demand in Labor Markets