Government Borrowing Affects Interest Rates in Financial Markets
How Does Government Borrowing Affect Interest Rates in Financial Markets?
- Marketing, Advertising, Sales & PR
- Accounting, Taxation, and Reporting
- Professionalism & Career Development
-
Law, Transactions, & Risk Management
Government, Legal System, Administrative Law, & Constitutional Law Legal Disputes - Civil & Criminal Law Agency Law HR, Employment, Labor, & Discrimination Business Entities, Corporate Governance & Ownership Business Transactions, Antitrust, & Securities Law Real Estate, Personal, & Intellectual Property Commercial Law: Contract, Payments, Security Interests, & Bankruptcy Consumer Protection Insurance & Risk Management Immigration Law Environmental Protection Law Inheritance, Estates, and Trusts
- Business Management & Operations
- Economics, Finance, & Analytics
How Does Government Borrowing Affect Interest Rates in Financial Markets?
Assume that government borrowing of substantial amounts will have an effect on the quantity of private investment. How will this affect interest rates in financial markets?
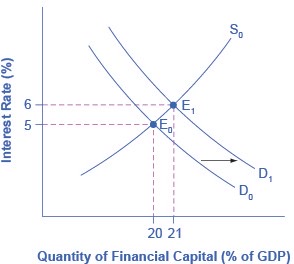
In the financial market, an increase in government borrowing can shift the demand curve for financial capital to the right from D0 to D1. As the equilibrium interest rate shifts from E0 to E1, the interest rate rises from 5% to 6% in this example. The higher interest rate is one economic mechanism by which government borrowing can crowd out private investment.
A survey of economic studies on the connection between government borrowing and interest rates in the U.S. economy suggests that an increase of 1% in the budget deficit will lead to a rise in interest rates of between 0.5 and 1.0%, other factors held equal. In turn, a higher interest rate tends to discourage firms from making physical capital investments. One reason government budget deficits crowd out private investment, therefore, is the increase in interest rates. There are, however, economic studies that show a limited connection between the two (at least in the United States), but as the budget deficit grows, the dangers of rising interest rates become more real.
At this point, you may wonder about the Federal Reserve. After all, can the Federal Reserve not use expansionary monetary policy to reduce interest rates, or in this case, to prevent interest rates from rising? This useful question emphasizes the importance of considering how fiscal and monetary policies work in relation to each other. Imagine a central bank faced with a government that is running large budget deficits, causing a rise in interest rates and crowding out private investment. If the budget deficits are increasing aggregate demand when the economy is already producing near potential GDP, threatening an inflationary increase in price levels, the central bank may react with a contractionary monetary policy. In this situation, the higher interest rates from the government borrowing would be made even higher by contractionary monetary policy, and the government borrowing might crowd out a great deal of private investment.
Alternatively, if the budget deficits are increasing aggregate demand when the economy is producing substantially less than potential GDP, an inflationary increase in the price level is not much of a danger and the central bank might react with expansionary monetary policy. In this situation, higher interest rates from government borrowing would be largely offset by lower interest rates from expansionary monetary policy, and there would be little crowding out of private investment.
However, even a central bank cannot erase the overall message of the national savings and investment identity. If government borrowing rises, then private investment must fall, or private saving must rise, or the trade deficit must fall. By reacting with contractionary or expansionary monetary policy, the central bank can only help to determine which of these outcomes is likely.
Related Topics
- What is Government Spending?
- Autonomous Spending
- Autonomous Consumption
- Fiscal Policy
- Expansionary Fiscal Policy
- Contractionary Fiscal Policy
- Progressive vs Regressive Tax
- Marginal Tax Rates
- Proportional Tax
- Trickle Down Theory
- Discretionary Fiscal Policy
- Automatic Stabilizers
- Effects of Discretionary Policy (Interest Rates & Lags)
- Crowding Out Effect
- National Debt
- Government Borrowing
- Golden Rule
- Ricardian Equivalence
- Balanced Budget - Deficit and Surplus
- National Debt
- Standardized Employment Budget
- Deficit Hawk
- Austerity
- Twin Deficits
- Fiscal Policy and the Aggregate Supply and Demand Curve
- Stabilization Policy
- Robin Hood Effect
- Ricardo Barro Effect
- Automatic Stabilizers
- Standardized Employment Budget
- How Does Fiscal Policy Affect Interest Rates?
- Crowding Out
- Types of Lag in Fiscal Policy
- Temporary and Permanent Fiscal Policy
- Limitations of Fiscal Policy?
- How Politics Affects Discretionary Fiscal Policy
- Government Borrowing
- National Savings and Investment Identity
- Debtor Nation
- Fiscal Policy Affects Trade Balances
- Twin Deficits
- Exchange Rates Affect Budget and Trade Deficits
- What are the risks of chronic large deficits in the United States?
- How Fiscal Policy Can Affect Trade Imbalances
- Government Borrowing Affect Private Savings
- Ricardian Equivalence
- Fiscal Policy Affects Investment and Economic Growth
- Crowding Out of Physical Capital Investment?
- How Does Government Borrowing Affect Interest Rates in Financial Markets?
- Government Investment in Physical Capital
- Public Investment in Human Capital
- Fiscal Policy Can Affect Technology Development
- Economic Cycle or Business Cycle
- Business Cycle Indicator
- Peak and Trough
- Recession and Depression
- Hard Landing vs Soft Landing
- Economic Bubble
- Boom and Bust Cycle
- Great Depression
- Baby Boomer Age Wave Theory
- Skyscrapper Effect (Economics)
- V-Shaped Recovery
- W-Shaped Recovery
- U-Shaped Recovery
- Kondratieff Wave Cycle
- Contagion
- Feedback Rule Policy
- American Customer Satisfaction Index
- CNN Effect
- Bureau of Economic Analysis
- Business Starts Index
- American Recover and Reinvestment Act
- Abenomics
- Emergency Economic Stabilization Act of 2008
- Commodity Credit Corporation
- Humphrey Hawkins Act