Tax Incidence - Explained
What is a Tax Incidence?
- Marketing, Advertising, Sales & PR
- Accounting, Taxation, and Reporting
- Professionalism & Career Development
-
Law, Transactions, & Risk Management
Government, Legal System, Administrative Law, & Constitutional Law Legal Disputes - Civil & Criminal Law Agency Law HR, Employment, Labor, & Discrimination Business Entities, Corporate Governance & Ownership Business Transactions, Antitrust, & Securities Law Real Estate, Personal, & Intellectual Property Commercial Law: Contract, Payments, Security Interests, & Bankruptcy Consumer Protection Insurance & Risk Management Immigration Law Environmental Protection Law Inheritance, Estates, and Trusts
- Business Management & Operations
- Economics, Finance, & Analytics
What is a Tax Incidence?
Tax incidence means the extent to which a tax burden imposed by the government is shared between consumers and producers of the good or service subject to the tax.
Tax incidence commonly arises in the context of taxes on alcohol, tobacco, and imported items.
Using Elasticity to Determine Tax Incidence
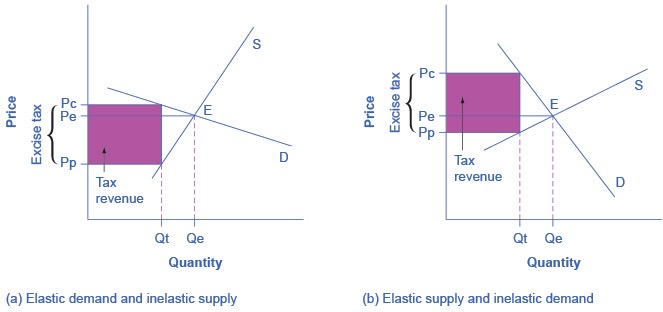
When the government implements a tax on a demand elastic good the tax incidence is primarily born by the producer. Conversely, a tax on a demand inelastic good is born by the consumer.
The situation is slightly more complex with supply elastic and inelastic goods and producers. If the supply is elastic, the producer of goods could re-organize their business and sell something other than the elastic good. So, they could avoid or shift the tax to others.
If the supply is inelastic, then the producer cannot alter their production or business organization easily. They will bear the majority of the tax and thus accept the lower price (or profits) for selling the same quantity.
If the supply was elastic and sellers had the possibility of reorganizing their businesses to avoid supplying the taxed good, the tax burden on the sellers would be much smaller. The tax would result in a much lower quantity sold instead of lower prices received.
Related Topics
- Elasticity
- Perfect, Zero, Infinite, and Constant Elasticity
- Elasticity of Demand
- Elasticity of Supply
- Price Elasticity of Supply and Demand
- Tax Incidence
- Cross Elasticity of Demand
- Cross-Price Elasticity of Demand
- Raising Prices Affect Revenue
- Price Sensitivity
- What is Elasticity and Tax Incidence?
- Short Run
- Elasticity of Savings
- Income Elasticity of Demand